China leads the way to the global renewable energy revolution
According to a newly published report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar is boosting the growth of renewables in global capacity, with China leading the way as the dominant global player.

According to a newly published report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar is boosting the growth of renewables in global capacity, with China leading the way as the dominant global player.
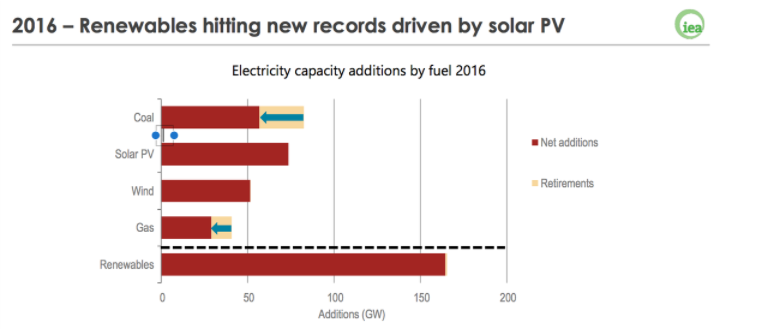
More specifically, “Renewables 2017” revealed that photovoltaics grew faster than any other fuel in 2016 due to increasing cost reductions and policy support.
Renewables accounted for an impressive 65 percent of new net electricity capacity additions, with approximately 165GW clean energy capacity coming online in 2016.
Source IEA
Solar capacity grew by 50 percent in comparison to 2015, reaching over 74GW; half of it attributed to China.
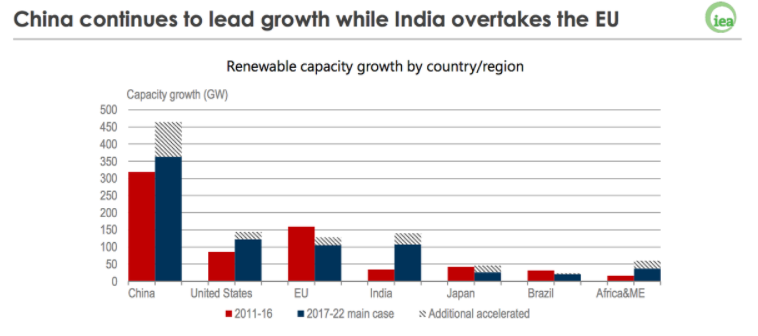
In a projection for the period between 2017- 2022, IEA predicts that global renewable electricity capacity will expand by over 920GW, an increase of 43 percent from 2016.
The prediction is more optimistic than last year's one, as IEA formed the bedrock of the forecast based on China’s impressive performance in 2016.
China alone accounted for 40 percent of the global growth of renewables, mainly driven by policies to tackle the county’s air pollution problem and ambitious capacity targets outlined in the 13th five-year plan to 2020.
Source IEA
The county has already reached and surpassed the solar targets for 2020 and is expected to reach the wind targets by 2019.
China is also considered a critical actor in the market development and decreasing costs of solar PV worldwide.
Currently, the country represents half of global solar PV demand, while Chinese companies account for around 60% of total annual solar cell manufacturing capacity globally.
This means that any market and policy developments in the country will have implications for demand, supply and prices all over the world.
Two important challenges that China will have to address are the growing cost of renewable subsidies and the issue of grid integration.
China is already moving away from its Feed-in Tariff programme to a quota system and green certificates, and new transmission lines and the expansion of distributed generation are expected to facilitate the integration of renewables in the electricity regime.
The United States remains the second-largest growth market for renewables, with growth driven by multiyear federal tax incentives combined with renewable portfolio standards and state-level policies for distributed solar PV, like California and Hawaii.
Nevertheless, political uncertainty over proposed tax reforms, international trade, and energy policies could have implications for the future growth.
In the European Union, the forecast for 2022 is 40 percent lower compared to the previous 5 year period, due to weaker electricity demand and overcapacity.
Hope remains for the Renewable Energy Directive covering the post-2020 period to address this challenge, improving market predictability for investors.
You can access the Executive Summary of the “Renewables 2017: Analysis and Forecasts to 2022” report here.